
HMI Training in India
- Real-Time Experts Sessions
- LIVE Project
- Certification
- Affordable Fees
- Flexibility
- Placement Support
HMI stands for human-machine interface and refers to a dashboard that enables a user to communicate with a machine, computer program or system. Technically, you could apply the term HMI to any screen that someone uses to interact with a device, but it’s typically used to describe such screens used in industrial settings. HMIs display real-time data and allow a user to control machinery using a graphical user interface.
Tech Cluster is an institute which provides HMI training in Indore and offers chances to avail a great opportunity to learn the tool from basic to advanced level. Our expert faculties cover all the important factors of HMI Training for beginners and intermediates. With our expert guidance students can excel in their career and earn good. After which you can find good opportunities in MNC Industries.
Course Highlights:
HMI Foundation :
- Understand the basics of a Human Machine Interface
- Build a fully functional HMI Program
- HMI Functionality Basics and Advanced Features
- Interface HMI with a PLC Program
- Design Criteria for HMI
How to Select an HMI
Duration :
- 45 Hours Theory
- 45 Hours Practical
- 20 Hours Project work
Technical Features:
Understand the basics of a Human Machine Interface
A Human-Machine Interface (HMI) is a user interface or dashboard that connects a person to a machine, system, or device. While the term can technically be applied to any screen that allows a user to interact with a device, HMI is most commonly used in the context of an industrial process.

Build a fully functional HMI Program
HMI Programming is different from most other programming languages. The reason is that an HMI is a visual representation of what’s happening on the manufacturing floor. Therefore, the actual HMI programming is typically referred to as HMI development as most of the time is spent on designing the layout of the screens rather than writing code in the traditional sense of the definition
Furthermore, the programming that will control the inputs and outputs of an HMI will generally reside on the PLC, giving the PLC programmer most of the control over the functionality of how the HMI will operate. However, both of these functions are combined at most facilities, and the PLC programmer would either create the layouts of the HMI screens or be familiar enough with the process to dictate how HMI programming will take place.

HMI Functionality Basics and Advanced Features
The most basic HMI will allow the operator to see the current status of a particular process. Imagine for a second that you have a grinding machine that you may start and stop with the press of either button. An HMI could be created to give a visual indication of the current status of the machine: stopped or running. However, a PLC could pull a lot more information from this machine, depending on the needs of the operation. Therefore, the HMI could be used to convey this information to the operator and allow him to make better decisions with regards to the process. HMI could include advanced features of the process such as batch controls, recipe management, line status, and much more.
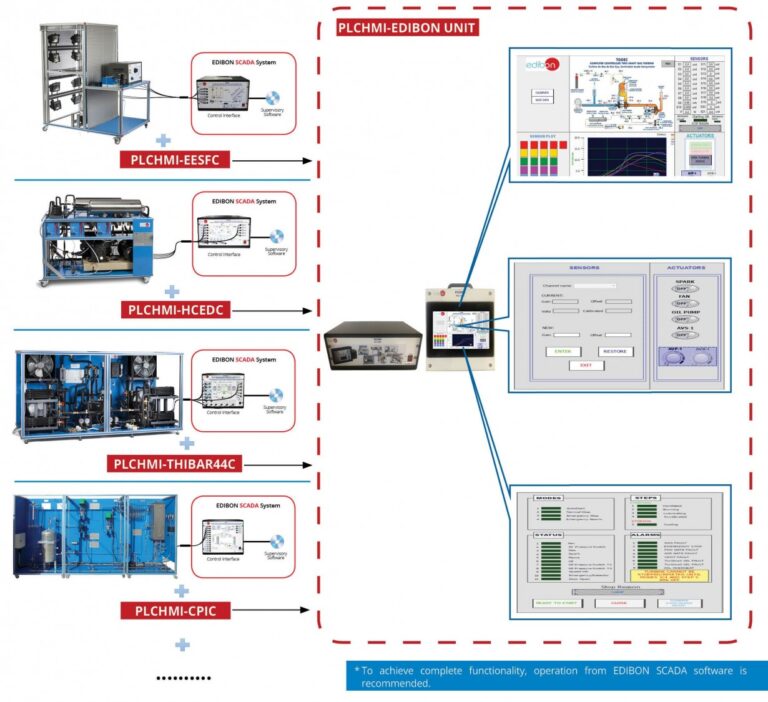
Interface HMI with a PLC Program
- Connect a serial port from the PC running the HMI programming software to the HMI serial port used for programming.
- Connect the HMI port for PLC communication to the PLC port used for HMI communication.
- Run the HMI programming software
- Follow the software steps to select the serial port to be used and the type of PLC to be interfaced with.
- Export the tag database file from the PLC.
- Import the tag database to the HMI software
- Create a new screen with some objects.
- Assign properties to the screen objects
- Save the project file and upload to the HMI display
- Test your program by touching a screen object and observing the expected action in the PLC.
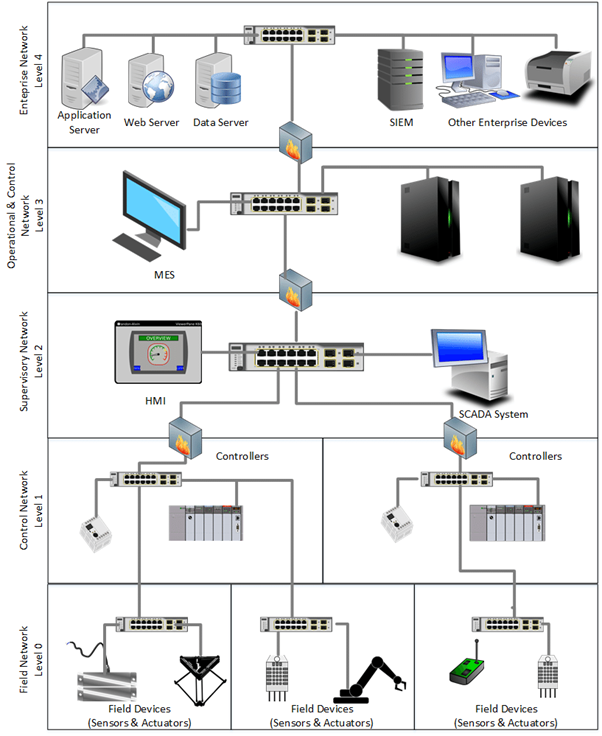
Design Criteria for HMI
Their are four Criteria for HMI Design-
1.HMI Hardware-The HMI hardware performs in a substation environment. The most common issue that should be addressed is whether a commercial personal computer, industrial computer, substation hardened computer, or server is required.
2.HMI Software-HMI software can be divided into the following three categories:
- Operating system software
- Application software that includes any application loaded on the computer
- Configuration file(s) for the settings, displays, and database of the HMI application.
3. HMI Screen-The HMI application provides a series of screens or windows for the monitoring and control of substation devices.
4. HMI Control Capabilities-The HMI application includes the capability of controlling equipment. The designer shall specify if HMI control is required.When control capabilities are required, they may include a combination of at least the following:
- Keys and switches (alphanumeric or function, or both)
- Cursor (mouse, trackball, or key controlled).
- Poke points (defined display control selection points)
- Pull-down or pop-up menus
- Physical switches, meters, lights, etc.

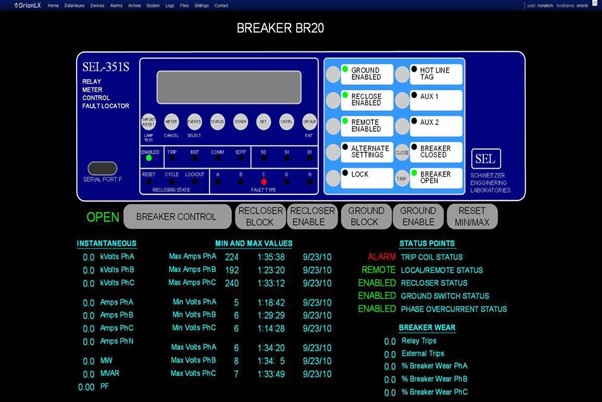
How to Select an HMI
An HMI is a substantial purchase, so it is important to know exactly what is required of it. HMIs typically perform one of three primary roles: a pushbutton replacer, a data handler, or an overseer. The pushbutton replacer HMI takes the place of LEDs, On/Off buttons, switches, or any mechanical device that performs a control function. The Data Handler is used for applications that require constant feedback and monitoring. Often, these data handlers come equipped with large capacity memories. The overseer works with SCADA and MES, centralized systems that monitor and control entire sites or complexes of large systems spread out over large areas. An overseer HMI is usually linked to the SCADA system’s databases and software programs, to provide trending, diagnostic data, and management information.

Upcoming Batches
Certifications

Reviews

















