Book Your Seat Now
Computer Aided Engineering (CAE)
Introduction -
Design and manufacturing is very vital to the progress of civilization. Before we dig deeper into CAE, let us first understand the basics of engineering design.
Engineering design of a product can be broken into four steps:-
Problem definition – in the initial stages of product development, it is necessary to clearly define what the product is meant to achieve and / or do.
Creative process – once the objective of the product is identified, it is necessary to synthesize its form. This involves brainstorming sessions where designers and engineers meet and interact. Various forms are evaluated and selected into a set of few workable solutions.
Analytical process – Fitting the product into form is the next step. This requires strength and reliability analysis, cost determination, etc. This step is very important and iterative. Multiple solutions for the product may be evaluated till the optimal values are achieved. This is where able to evaluate various parameters of the desired object.
Prototype development & testing – this is where the theory is translated into practical. Prototypes are developed and tested, usually.

Computer Aided Engineering (CAE)
Computer Aided Engineering (CAE) is a fast emerging field that takes CAD to another level.
While CAD is useful in creating 2D and 3D models of a product, CAE software allows a deeper engineering analysis of objects.
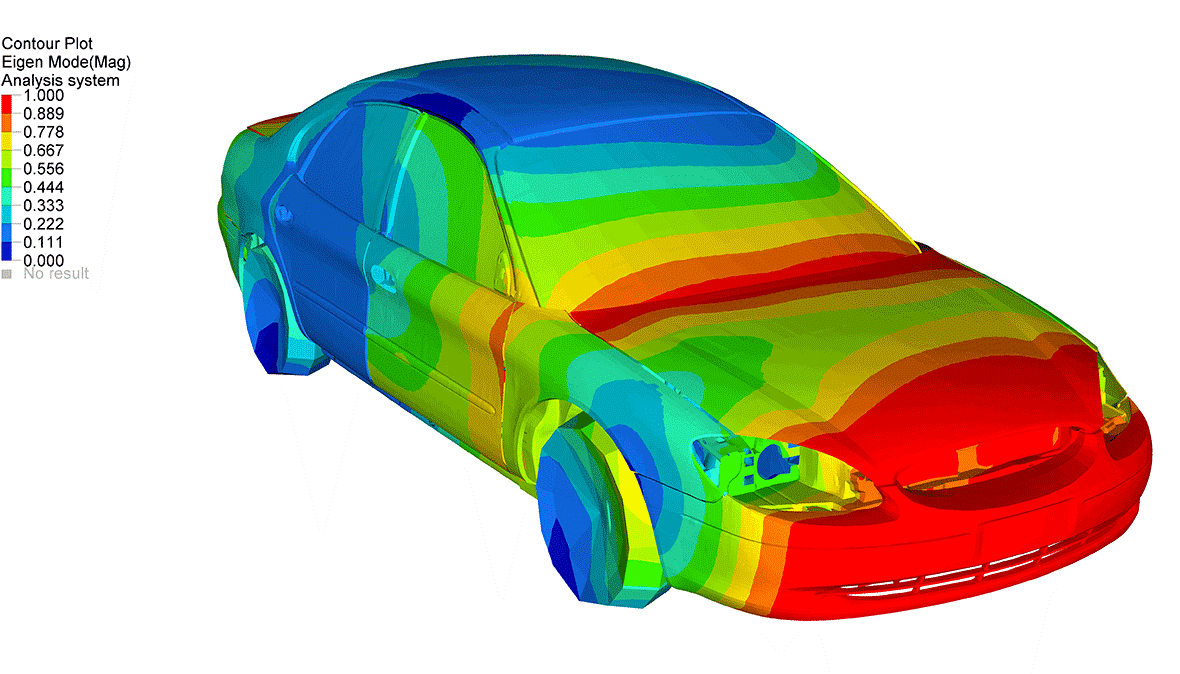
CAE thus finds applications in engineering fields like fluid dynamics, kinematics, stress analysis, finite element analysis, etc., typically where product development is concerned. CAE encompasses not only CAD, but also Computer Aided Manufacturing (CAM), Finite Element Analysis (FEA), Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) and some other aspects of engineering. Simply put, you can create 2D and 3D objects using CAD, while you can analyze how that object will behave using CAE tools. The automated design tools provided by CAE have transformed engineering analysis from a ‘hands on’ experience to virtual simulation.
The CAE Process
In the first stage, the object / product / system is designed, typically system being evaluated. These parameters include the physical properties, geometry and the limitations under which the entity is to be developed. In the second stage, the entity is thoroughly evaluated using CAE processes like FEA, NVH (noise, vibration and harshness), CFD, etc. As a third step, the results are shown to the engineering design team and the parameters of the system / object are tweaked to get optimum results. The process is iterated till the desired benefits are achieved.
Benefits of CAE
- Since simulating reality is less time consuming, CAE processes save on time and money.
- CAE reduces the errors in design and drawing process.
- The impacts of changing parameters on a system can be studied with more accuracy.
- Robustness and performance of components and assemblies can be analyzed.
- CAE allows for easy visualization and improves designs CAE aids ease of manufacturing.
- Tools of the Trade Since there are several aspects of engineering that need to be covered while designing / modelling a system or entity, there are many facets .
CAE Training
As computational power grows, CAE tools are becoming increasingly powerful. There are many parameters that software like CATIA and HyperMesh offer that it is virtually impossible to master it easily. This is where CAE (and CAD) training institutes come into play. Reputed institutes have experienced instructors who introduce students to the http://techcluster.co.in/at Indore, India) have tie ups with manufacturing industries to let their students get a ‘hands on’ experience with live projects


